Research within this vision has been supported by NATO’s “Science for Peace and Security” program. The project was an attempt to provide such an integrated system for emergency support in urban areas.
Vision
- Planning how to handle acute crises at the urban level caused by extremely high levels of pollution as well as pollutants released during terrorist attacks within the urban environment.
- The impact of simulation tools and modeling is very high, both in economic and social conditions. The availability of these tools can lead to great cost savings and protection of human lives.
- Examining the impact of spatial parameters on aeration conditions. Develop mathematical methods for their assessment and for optimizing urban planning in order to reduce the effect of the spread of pollutants in urban areas.
Purpose
- Support emergency services and decision makers. Provide access to and insight into the real-world database of a wide range of geographic information and simulation model results so that adequate countermeasures are better distributed accordingly. This is necessary in order to assess the impact at the social level.
- Training all employees to ensure less risk of exposure during the crisis period.
- Gaining access to such a simulation model for the necessary preparations due to a terrorist attack or the spread of contamination and the placement of certain protection measures.
- To have access to an appropriate decision support system in order to facilitate the situation after the accident at the urban level in all parameters.
Contributions
- Work has resulted in certain scientific, engineering and educational results for years
- Contribution and review of systematization of knowledge related to basic mathematical models of gas pollutant dispersion.
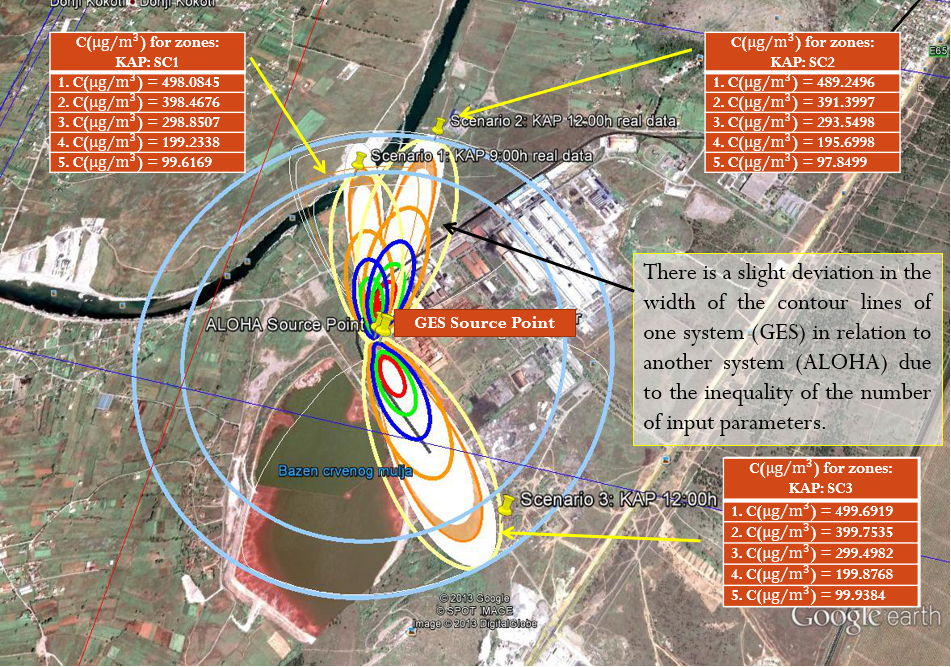
- Integration and execution of an advanced model in order to increase the accuracy of the system by the number of input parameters.
- Realization of software support that enables direct insight into the amount of pollution with appropriate values of concentrations.
- Comparison of the realized model with the already existing one (eg ALOHA) for the purpose of insight into its adequacy as well as its accuracy.
- Visualization of the problem and presentation of several excessive situations (KAP, TPP Pljevlja).
- Solutions to the problem of dispersion of gaseous pollutants from industrial chimneys. Presentation of adequate guidelines for future work in this field and others like it.
- Detailed analysis of mathematical models and dispersion processes. Hardware-based software solutions that can be used to analyze similar or other problems for educational purposes.